- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- Video Tutorial »
- How to Block-in Hair on Your Acrylic Portrait
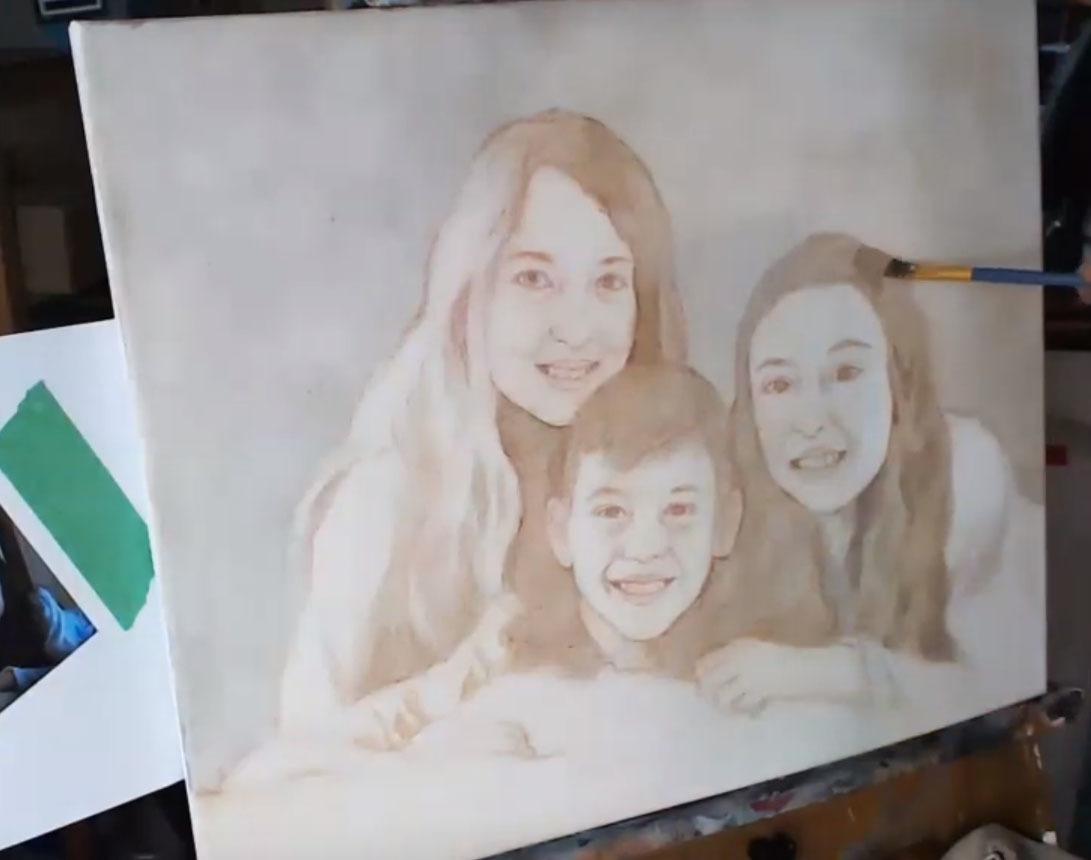
How to Block-in Hair on Your Acrylic Portrait
The steps to block-in hair, adding depth and realism with layered glazing techniques.
When creating a realistic portrait, the process of blocking-in hair plays a crucial role in establishing depth and capturing lifelike textures. In this tutorial, you will learn step-by-step how to block in hair on an acrylic portrait . By following these essential techniques, you’ll discover how to mix tones, apply glazes, and build up layers to make your portrait more three-dimensional.
Understanding the Block-in Process for Hair
Before diving into the specifics, it’s essential to understand the “block-in” technique. Blocking-in refers to the initial stage where you establish basic shapes, values, and shadows before adding detailed layers. This foundational stage is critical for creating a structured framework for your portrait, ensuring that as you add more layers, the hair appears realistic, cohesive, and well-blended.
Step 1: Establishing the Background and Hair Boundaries
The first step in blocking-in hair is defining the broader sections of the portrait. In the video, I start by setting up a muted, cloudy background. Using colors like ultramarine blue and raw umber dark, blends these shades to create a smooth transition from cooler to warmer tones. Because this method can also apply to your portrait’s background, ensuring the hair and face blend seamlessly into the backdrop without looking disconnected.
Once your background is set, begin focusing on the hair. Start by identifying the boundaries and large sections of hair. At this stage, do not worry about small details like individual strands; instead, focus on the bigger shapes and how the hair flows around the face and neck.
Step 2: Darkening the Hair with Cool Tones
To create depth, it is essential to start with darker tones. I recommend that using a mixture of raw umber dark and ultramarine blue for the base layer. By adding the blue, you cool down the mix, which is vital when working with shadows. The darker, cooler tones help create the illusion of depth, mimicking the way light interacts with the hair in dimly lit areas.
As I explain, the cooler tones mimic the appearance of shadows when light is scarce. The mixture of ultramarine blue and raw umber dark serves as the ideal “Payne’s gray” substitute, but with more versatility since you can customize the shade based on your needs. Apply this mixture lightly over the larger sections of hair, focusing on the areas that will remain in shadow.
Step 3: Defining Local Values and Shapes
Once the darker base coat is applied, it’s time to define the local values. Local values refer to smaller, nuanced changes in light and shadow. Instead of focusing on the entire area, look for pockets of darker tones that indicate hair bends, waves, or areas where light is blocked.
For example, the hair under the chin or near the ear will often feature shadows. I use precise brushstrokes to form the shadowed sections, while leaving lighter areas untouched to create contrast. This helps in defining the unique shapes that hair takes on.
Use a fine-tipped brush to enhance the details and smaller sections. At this stage, you don’t need to be exact, but try to match the general direction and flow of the hair. Your initial layers are meant to be flexible, allowing you to adjust later.
Step 4: Gradation and Layering for Hair Striations
Acrylic portraiture thrives on the glazing technique, which involves building layers of translucent paint to achieve a gradual change in value. In this step, focus on blending your dark tones into lighter ones by applying thin layers of glaze. I use clear medium to thin his paint and slowly introduces gradation into the hair.
To add natural-looking striations (the small, subtle streaks of hair), use the tip of your brush and apply long, delicate strokes. These strokes should be thin and follow the natural grain of the hair. Remember to vary the pressure on your brush. For darker areas, apply more pressure, while lighter sections need less to avoid over-darkening.
Step 5: Highlighting Key Areas and Adding Definition
After laying down the foundational layers and working on the shadows, the next step involves highlighting. In the reference image, I notices that there’s a distinct highlight at the top of the hair. Using a slightly lighter mixture of raw umber dark, he begins to emphasize these sections.
To create highlights, focus on the areas where light naturally hits the hair such as the crown, or where the hair parts. A light touch with a fine brush can enhance these areas, bringing dimension and texture. Be careful not to overdo the highlights; subtlety is key.
For instance, adding a soft glaze using the clear medium allows you to leave some areas lighter. Later, you can apply a reddish glaze, which, as I take notes, will provide a ton of luminosity and help the hair “pop” out of the portrait with vibrant, warm tones.
Tips and Techniques for Effective Hair Block-in
- Use a Cool Base for Dark Hair: When blocking in darker hair, use cool tones mixed with raw umber and ultramarine blue. This ensures the shadowed areas appear more realistic and avoid a flat, monotone appearance.
- Vary Brush Strokes: For a natural hair texture, use different brush strokes long strokes for defining edges and shorter, dabbing strokes for blending. This combination will give your painting more depth and a smoother transition between light and shadow.
- Gradation is Key: Gradually build layers using the glazing technique. Thin out your paint with clear medium and apply transparent layers. This technique will allow you to adjust tones without overpowering the base layer.
- Pay Attention to the Reference Photo: Use the reference photo to determine where the highlights and shadows fall. Aligning shadows with landmarks like the lips, nose, or chin ensures proportional and accurate placement.
- Don’t Overdo Highlights: Highlights should be subtle. Too much highlighting can make the hair look unrealistic and take away from the depth created by the shadows.
Conclusion: Building Up for Realism
Blocking-in hair is all about establishing the basic framework before moving on to finer details. By using cool tones, creating gradation, and employing glazing techniques, you can achieve a realistic and lifelike portrayal of hair. Remember, the key is patience building up layers slowly ensures that the final result will have depth, texture, and vibrancy.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced painter, mastering the block-in process is crucial for creating beautiful acrylic portraits that stand out. Start with the shadows, define the mid-tones, and finish with highlights for hair that looks three-dimensional and natural.
For more tutorials and painting tips, visit RealisticAcrylic.com and take your portrait painting skills to the next level!
Did you enjoy this video?
Share it with your artist friends if you think they will find it helpful! Also, if you need more help, hop onto courses.realisticacrylic.com where we concentrate on just acrylic portraits, and how to make yours the best it can be.
My goal is to make your life as acrylic portrait artist easier by giving you tips, lessons, and tutorials.
Yours for Better Portraits,

If you found this post helpful or encouraging, would you send it on ahead? Let others know with the share buttons below. I’d love to hear your comments. Thank you so much!
